- Bariatric Surgery
- Cardiology
- Transplants
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Bladder Cancer Treatment
- Bone Cancer Treatment
- Breast Cancer Treatment
- Colon Cancer Treatment
- Esophagus Cancer Treatment
- Kidney Cancer Treatment
- Leukemia Treatment
- Liver Cancer Treatment
- Lymphoma Treatment
- Lung Cancer Treatment
- Myeloma Treatment
- Prostate Cancer Treatment
- Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
- Ovarian Cancer Treatment
- Testicular Cancer Treatment
- Orthopedics
Breast Cancer Treatment Cost in India
“The cost of Breast Cancer Treatment in India starts from $3000 (INR 228,000). This cost can be less or more depending upon the hospital, experience of doctors, quality and type of implant used and many more parameters.”
Breast cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the tissues of the breast. This uncontrolled growth of breast cells may take place in any part of the breasts.
It can either be benign or malignant. Benign tumors go slowly and do not invade other cells and tissues. A malignant tumor can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated and unchecked. The cost of Breast Cancer Treatment in India starts from $3000 in India.
|
|
Breast Cancer Treatment |
Price in (₹) |
Price in ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Chemotherapy |
Starting from INR 22,376 (per session) |
Starting from USD 600 (per session) |
|
2 |
Lumpectomy |
Starting from INR 223,761 |
Starting from USD 3,000 |
|
3 |
Radiation Therapy |
Starting from INR 261,000 |
Starting from USD 3,500 |
|
4 |
Radical Mastectomy |
Starting from INR 447,500 |
Starting from USD 6,000 |
|
5 |
Total Mastectomy |
Starting from INR 522,000 |
Starting from USD 7,000 |
Molly Mukonde from Zambia visited India with her husband for breast cancer treatment.
Molly’s husband expresses complete satisfaction with the services provided by Lyfboat and extends his gratitude to Dr. Surbhi. Thanks to the exceptional cancer treatment received in India, Molly is now cancer-free. During their time in India, they had the opportunity to meet numerous patients from various countries who had also come for cancer treatment.
Get a Free Personalized quote for Breast Cancer Treatment in India
Trusted by Patients from 90+ countries
- Connect with 1000+ Specialists
Use the built in communication tools to ask as many questions as needed and get a prompt response. Patient Coordinators will assist you from start to finish.
- Connect with Hospitals around the globe
We hand pick each hospital & only internationally accredited hospitals are included to ensure you will receive high quality care.
- Unbeatable Quotes - Guaranteed
If you receive a lower quote for the same treatment, hospital and doctor, we guarantee we will beat that price.
- Free Medical Advice from Experts
Speak directly to doctors to have all your questions and concerns addressed before finalizing where to get your treatment.
Factors affecting the cost of Breast Cancer Treatment in India
Chemotherapy and cancer medicines are expensive. But, compared to the western countries, India has less expensive and low-priced treatment for cancer patients. The cost of breast cancer treatment in India varies with cities and hospitals.
- Every hospital has its own treatment facilities, surgeons, and infrastructure. The cost of facilities charges and tests add up to the cancer treatment cost. India has all the facilities of helping overseas patients with the most affordable breast cancer treatment.
- High-quality breast cancer treatment is available in India and it is at par with what a medical tourist from abroad can avail in the US and the UK. But the benefit of choosing India over any other Western country is that treatment is available at a much lower price.
- Extensive imaging facilities, diagnostic services, CT technology, and advanced MRI are available in many Indian cities. The different techniques for breast cancer surgery and treatment are available at 80 percent lesser prices than the UK and US rates.
Even if the travel and lodging expenses of the patient’s family are taken into account, the cost of breast cancer is much lower. Here, have a look at the cost comparison.
The foreign countries from where patients often travel to India for cancer treatment include the UK, US, Afghanistan, Australia, Tanzania, Nepal, Lanka, Kenya, Zambia, Zealand, Ethiopia, Canada, Uzbekistan, Uganda, and Nigeria. It should be noted that the cost of cancer treatment in India is inclusive of stay in hospitals, surgery, consumables, medicines, airport transfers, and the free stay of the companion.
Note: The treatment costs vary from case to case and a specialist review is advised to determine the best procedure/approach for treatment. Several external factors also impact the cost & quality of treatment including the method of treatment, room category, and several other factors. Please contact Lyfboat Care Team for a personalized quote and advice.
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the tissues of the breast. This uncontrolled growth of breast cells may take place in any part of the breasts. Mostly, it affects women but males can also get breast cancer. It is the second leading cause of death among females in India.
The cancer of the breast can either be benign or malignant. Benign tumors go slowly and do not invade other cells and tissues. The latter type of breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated and unchecked. They proliferate quickly.
Formation of Cancer in Other Parts
In most cases, when we refer to “breast cancer,” we mean tumors that develop in milk ducts or lobules. Other breast regions are also susceptible to developing cancer, though less frequently. These may consist of:
Angiosarcoma: This uncommon kind of cancer starts in the cells that line blood arteries or lymphatic vessels.
Phyllodes tumors: Phyllodes tumors, which begin in the connective tissue, are uncommon. They are often benign (noncancerous), but occasionally they can be malignant (cancerous).
What are the types of breast cancer?
Breast cancer can be of different types, depending on the exact area of the breast where the uncontrolled growth of cells has taken place. Following are the list of Common breast cancer types:-
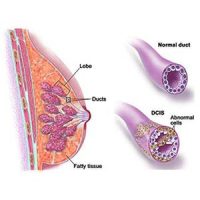
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is non-invasive breast cancer.
- It starts inside the milk ducts and it hasn’t spread to any normal surrounding tissues.
- Although DCIS is not life-threatening, it increases the risk of invasive breast cancer.
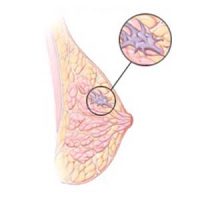
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)
- In Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC), cancer breaks through the wall of the milk-producing lobule and begins to invade the tissues of the breast.
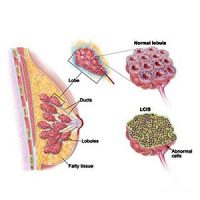
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS)
- Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is referred to when the abnormal cells start growing in the milk-producing lobules and do not spread to surrounding tissues. It increases a person’s risk of developing invasive breast cancer later on in life.
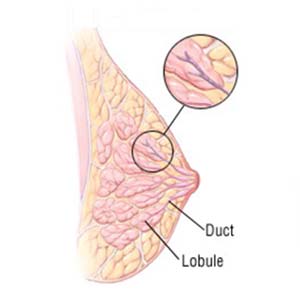
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is a very common type of breast cancer, about 80% of breast cancers are IDC. In this type, cancer breaks through the wall of the milk duct and starts spreading to the surrounding breast tissues. It can spread to the lymph nodes, if not treated on time. There are 5 types of IDCs as follows:-
- Tubular – The tumor is made up of tube-shaped structures called tubules.
- Mucinous – The tumor is a soft, fleshy mass that resembles the medulla.
- Papillary – The tumor is made up of cells that float in pools of mucin which is a key ingredient in mucus.
- Cribriform – The tumor has a well-defined border and is made up of small, finger-like projections.
- Medullary – The tumor has distinctive holes in between the cancer cells which make it look like Swiss cheese. In ICC the cells look and behave like normal, healthy breast cells.
Inflammatory breast cancer
- Inflammatory breast cancer is a very rare and aggressive disease in which lymph vessels in the skin of the breast are blocked by cancer cells.
- In this type, the breasts often look swollen and red or inflamed. Inflammatory breast cancer tends to grow rapidly, often in a matter of weeks or months.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
A woman may have breast cancer if she notices any of the disease’s telltale signs and symptoms. Because some symptoms may go unnoticed by patients, breast cancer screening and diagnosis are crucial. For those who can afford it, screening should be done every two years to be sure there are no signs of the disease.
Breast cancer is most often diagnosed in adults over the age of 50, but it can occur at any age.
The following are a few breast cancer and cell abnormality symptoms that need to be looked at, assessed, and found as soon as possible:
- A significant bulge caused by breastfeeding
- A change in the size, shape or contour of your breast.
- Either the breast cells or the breast skin has developed dimples.
- The breast location has reversed.
- Rashes or colour changes on the eyebrow to start growing
- Nipple Discharge/Uncontrollable fluid release (which can be either bloody or clear).
- Lump in the Breast or Underarm (as small as a pea).
- Pain in the Breast
- A marble-like hardened area under your skin.
What are the causes of breast cancer?
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, another name for breast cancer, is frequently brought on by cells in the ducts that produce milk.
- Breast cancer can begin in various cells or tissues within the breast, including the glandular tissue known as lobules (invasive lobular carcinoma).
Although uncommon, breast cancer can also strike men. - Compared to cisgender men, transgender women are more likely to acquire breast cancer. In addition, compared to cisgender women, transgender men had a lower risk of breast cancer.
- According to research, a person’s way of life, hormones, and environmental factors are all linked to their risk of developing breast cancer.
There may be some risk factors that are controllable and others are categorized as uncontrollable:
Risk Factors One Cannot Change
- Getting older.
- Being Female
- Genetic mutations.
- Reproductive history.
- Having dense breasts.
- Personal history of breast cancer or certain non-cancerous breast diseases
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer.
- Previous treatment using radiation therapy.
- Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy
Risk Factors One Can Change
- Not being physically active.
- Being overweight or having obesity after menopause. .
- Taking hormones.
- Reproductive history the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
- Drinking alcohol.
How to diagnose breast cancer?
There are several types of tests conducted for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Some of the common tests include the following:
- Ultrasound
- Mammography (X-ray of the breast)
- Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Breast Cancer Biopsy
A breast Cancer diagnosis is routinely conducted at all multispecialty and cancer hospitals. The tests such as biopsy, mammography, and ultrasound help confirm whether the patient is suffering from cancer or not. These tests help confirm the stage and grade of the tumor as well.
Once the cancer is confirmed, the doctor may order a few blood tests and the positron emission tomography (PET) scan to confirm whether the cancer is restricted to its place of origin or has spread to other parts of the body.
Based on the diagnosis made, a suitable treatment plan is tailored according to the needs of the patients.
How can Lyfboat assist you getting Breast Cancer Treatment Cost in India?
World's Most Trusted Medical Advisory & Discount Platform
Lyfboat is a free advisory platform; we do not charge any fees from patients. In fact, we negotiate the price that Indian hospitals offer. In some cases we are able to reduce the cost by negotiating upto 20% of what Hospitals generally offer. We advise the best treatment from the top hospital/surgeon at best price.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Stages of cancer progression:
One may hear certain words that are used for describing the different stages of breast cancer, which include local, regional, and distant. Local breast cancer term is used to describe cancer in the breast. Regional breast cancer indicates that the lymph nodes in the armpits have been affected as well. Distant breast cancer is spread to other parts of the body as well.
In medical terms, breast cancer is best categorized as Stage 0, Stage 1, Stage II, Stage III, and Stage IV. Stage 0 is the nascent stage and is defined as non-invasive breast cancer. There are no signs of cancerous or non-cancerous abnormal cells found in any part of the body, including the breasts.
Stage I breast cancer
Stage I is the preliminary stage when cancer cells have started to grow inside the breasts but they have not spread out to any other part of the body. Typically, no lymph nodes are involved in this stage.
Stage II breast cancer
Stage II is that stage where no tumor is found, but cancer breaks out in the lymph nodes. In this case, the tumor usually measures 2 centimeters. The tumor can be larger than 2 centimeters but is definitely smaller than 5 centimeters.
Stage III breast cancer
Stage III is described as invasive breast cancer. The tumor measures more than 5 centimeters in this case. cancer is diagnosed in four to nine axillary lymph nodes situated near the breastbone.
Stage IV breast cancer
Stage IV is the fatal stage where cancer has spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body into other organs like the brain, liver, lungs, skin, and lymph nodes. The words ‘’metastatic’’ or ‘’advanced’’ are used to describe Stage IV. Stage IV cancer may be the recurrence of previous breast cancer or it may be diagnosed for the first time.
What are the breast cancer treatment options available in India?
Following are the treatment options for breast cancer surgery in India:
Breast cancer surgery
Surgical intervention may be done for the following reasons:
- Remove as many cancer cells as possible – breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy
- Determine whether cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes under the arm – sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection
- Restore the shape and appearance of the breast after the removal of cancer – breast reconstruction surgery
- To relieve the symptoms of advanced-stage breast cancer
Breast cancer surgery in India has the following options:
- Lumpectomy or breast-conserving surgery: This procedure involves the removal of the part of the breast with a tumor only, along with a small amount of surrounding healthy breast tissue. It is also referred to as partial mastectomy or segmental mastectomy. The goal is to remove the cancer cells as much as possible, while still conserving healthy parts of the breast. The amount of breast tissue that will be removed majorly depends on the location and size of the tumor.
A far less common breast cancer removal surgery is a quadrantectomy. In this, almost a quarter of the breast is removed. After this surgery, the operated breast will appear smaller depending on the amount of tissue removed. It is sometimes referred to as a segmental excision.
- Mastectomy: It involves the complete removal of all the breast tissue. With advanced surgical techniques, this surgery has become more refined and less intrusive than it used to be earlier. Now, the muscles under the breast are no longer removed (radical mastectomy) in most cases.
There are different types of mastectomy procedures available, such as skin-sparing mastectomy (skin can be preserved), or a nipple-sparing mastectomy (the nipple can be preserved).
Some women may need the removal of both of the breasts, which is known as a double mastectomy.
Radiotherapy is also administered as adjuvant therapy after the surgery if there is a risk of relapse or recurrence.
Lymph node removal: It can be performed during a lumpectomy and mastectomy if the biopsy results indicate that breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- Sentinel lymph node dissection or biopsy: In this, the surgeon locates and removes one or a few lymph nodes from under the arm. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the breast area and the first nodes to which cancer can spread. This is a less-invasive which helps in avoiding the removal of multiple lymph nodes with an axillary lymph node dissection. Removing the lesser number of the lymph nodes in this procedure helps lower the risk of several side effects of the surgery, including lymphoedema (arm swelling).
- Axillary lymph node dissection: This procedure involves the removal of several lymph nodes from under the arm. The number of lymph nodes removed in an axillary lymph node dissection varies for different patients. It may not be required for all women with early-stage breast cancer who have small amounts of cancer in their sentinel lymph nodes. A full axillary lymph node dissection is generally avoided in women having a lumpectomy and radiation therapy, and those who have a smaller tumor and not more than 2 sentinel lymph nodes have cancer. It is to reduce the risk of side effects of the procedure without affecting survival.
- Breast reconstruction: This is a procedure to rebuild the breast after a surgery – mastectomy and sometimes lumpectomy. Breast reconstruction can be performed at the same time as cancer-removing surgery, this is known as immediate reconstruction, or months to years later, called as delayed reconstruction. There are different options for reconstruction, including a prosthesis or tissue flap procedure. Many women having mastectomy surgery for breast cancer will have the option of breast reconstruction. The aim is to restore the natural appearance of the breast after surgery. For some patients undergoing breast-conserving surgeries, the doctor may suggest grafting fat into the affected breast to cover any dimples left after the surgery. There are several types of reconstructive surgery, and a woman may choose a certain reconstruction option depending on the individual preference and medical condition.
Breast implant: These are prosthetic devices that are placed under the skin to give a natural appearance of the breast. The two most common types of implants are saline-filled or silicone gel-filled. The saline-filled implants have an outer shell made up of silicone and filled with sterile saline or salt water inside. A silicone gel-filled implant is filled with silicone gel instead of saltwater. There are several other types of implants with different shapes and textures. Each implant has its own benefits and risks. The choice of the implant varies from person to person.
Tissue flap procedure: In this method, the surgeon uses muscle and tissue taken from other parts of the body to reshape the breast. A tissue flap surgery can be done using the tissue from the back or belly, called a pedicle flap. This flap is transferred to the chest without cutting any blood vessels. A free flap procedure means the surgeon cuts the blood vessels and the moved tissue is attached to the new blood vessels in the chest.
The oncologist may also suggest prophylactic procedures to reduce the risk of cancer –
- Prophylactic mastectomy: It is a preventive procedure in which the breast is removed to lower the risk of breast cancer in people who are at high risk.
- Prophylactic ovary removal: This is a preventive procedure to reduce the amount of estrogen in the body. It aims to make it less likely for estrogen to stimulate or aid in the development of breast cancer.
Chemotherapy –
It administered either before or after breast cancer surgery. It involves the use of specific drugs to kill off cancer cells. The use of chemotherapy may depend on the stage and the location of the cancer. Different doses of chemotherapy drugs are administered through injections directly into the veins or with the help of an IV solution or pills. The motive is to kill the cancerous cells and impede further relapse.
Radiation therapy –
It is often done post-surgery to kill the cancerous cells that are still left. Radiation therapy is done in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of invasive breast cancer.
Types of Radiotherapy for breast cancer treatment:
External beam radiation: It is the most common type of radiation therapy used for breast cancer patients. In this, radiation is delivered by a machine outside the body which focuses the radiation beams on the targeted area having cancer.
Women who had lumpectomy will most likely have radiation to the entire breast, referred to as whole breast radiation.
The standard radiotherapy schedule for whole breast radiation is about 5 days a week for about 6 to 7 weeks. Another option for this therapy is hypofractionated radiation therapy in which the radiation is given to the whole breast, but in larger daily doses and with fewer cycles, typically for only 3 to 4 weeks.
Partial breast irradiation is also an option for some women, in which larger doses of radiation are given over a shorter time to only a selected part of the breast, instead of the entire breast.
Other types of radiation therapy for breast cancer:
- Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT): This treatment involves administering a single large dose of radiation to only the area from where the tumor was removed in the operating room. It is performed right after a Breast-Conserving Surgery, just before the incision on the breast are closed.
- 3D-conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT): It is an advanced radiation technique, in which special machines are used to accurately aim the radiation at the area from where the tumor was removed. This helps to prevent damage to the healthy breast tissues.
- Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT): This is also an effective radiation delivery method, like 3D-CRT. It involves changing the strength of the radiation beams in certain areas, to allow stronger doses to certain parts of the breast. This helps lessen the damage to surrounding healthy body tissues.
- Brachytherapy: This is an internal radiation technique. In this treatment, radiation beams are not aimed from outside the body, but a device containing the radioactive seeds or pellets is directly placed into the area of the breast where cancer had been removed, for a short period of time. Brachytherapy is an option for selected cases depending on factors such as tumor size and location.
Hormonal therapy –
It is administered on PR-positive and ER-positive types of patients with breast cancer. The idea is to give hormonal therapy medicines so as to obstruct the action of hormones on the cancer cells and stop their further proliferation.
Targeted drug therapy –
It is the most advanced type of treatment for breast cancer. It is expensive but result-oriented. Targeted drug therapy is different from chemotherapy wherein certain characteristics of the cancer cells are targeted. For example, the presence of HER-2 receptors on the surface of the cancer cells in the case of breast cancer. These cells tend to grow abnormally and so are specifically killed by targeted drug therapy. Unlike chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy does not kill healthy cells in the body.
Procedure and Recovery
- Depending on the status and stage of the malignancy, as well as the type of operation performed, the patient will need to stay in the clinic for a number of days.
- Total recuperation can take a few months, and for individuals in the advanced stages, it may take a little longer.
- To ascertain whether the tumor’s cell count has returned, routine follow-up exams and assessments will be necessary.
- The patient will have to deal with various side effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, including as fatigue, nausea, weight loss, and hastened hair loss.
- The usage of medication can lessen these symptoms, which will also make things simpler for the patient.
- A person should see a doctor if symptoms such as unsettled stomach, loss of desire, unexpected menstruation, weariness, back pain, rapid weight loss, prostate problems, stomach discomfort, bloating, etc. recur and remain stable for protracted periods of time.
Precaution as Prevention
How do I know whether the cancer will be detected before it spreads?
While breast cancer cannot be prevented entirely, there are several things patients can do to lessen the likelihood of finding it when it is well advanced. For instance:
- Schedule regular mammograms. It is advised to start screening mammograms at age 35 and continue them annually after turning 40.
- After the age of 20, check your breasts every month. One becomes familiar with the contours and feel the breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- After the age of 20 and every year after the age of 40, have your breasts inspected by a medical professional. Mammograms may miss lumps that are detected during clinical breast exams.
What is the breast cancer survival rate?
- 90% of breast cancer patients survive the disease after five years. In other words, 90% of those who receive a diagnosis of the condition are still living five years later.
- While metastatic breast cancer has a 28% five-year survival rate, localized breast cancer has an 86% five-year survival rate.
- Fortunately, with increased understanding along with development of new and better management strategies, breast cancer survival rates are improving.
- Take into account that survival rates are simply approximations. They are unable to forecast treatment outcomes or estimate your life expectancy.
- It’s imperative to speak with the oncologist in case of any particular inquiries about the survival rates for breast cancer.
Early-stage breast cancer patients in India frequently successfully manage their illnesses with treatment. In real terms, a lot of people who are diagnosed with breast cancer go on to lead lives that are fulfilling and productive.
Why choose India for breast cancer treatment?
India houses some world-class hospitals for breast cancer treatment. These hospitals offer state-of-the-art treatment and diagnostic facilities, which includes the use of high-end and the latest technology. The affordable mammogram cost and breast cancer treatment cost charged by the hospitals makes patients come to India for medical treatment. The cost is just one-fifth of what it costs in other countries, like UK, US, and UAE.
There are many reasons why patients from abroad feel confident and safe while traveling to India for breast cancer treatment. Some of the reasons include the following:
- The facilities offered at the breast cancer hospitals adhere to national accreditation standards and that of international hospitals.
- The staff employed at the top hospitals for breast cancer treatment in India are fluent in English.
- The doctors understand the needs of the patients quite well.
- Top doctors in India make use of third generation technology plus medical techniques for patients.
- A loving and compassionate environment is the unique selling proposition of Indian hospitals.
- The best hospitals boast of the most eclectic group of surgical oncologists combined with the medical team.
- The surgeons possess the expertise and skills required for solving the simplest to the most complicated cases.
There are several multi-facility and super-specialty Indian breast cancer treatment hospitals. All types of cancers are treated through application of cutting-edge technology. The main goal is to focus on the specific needs of patients and design a treatment procedure suited for the particular patient.
List of some Indian breast cancer hospitals include the following:

Max Super Specialty Hospital
Saket, New Delhi, India
Max Super Specialty Hospital
Saket, New Delhi, India
Best Doctors for Breast Cancer Treatment in India
India is globally renowned for its brigade of highly experienced oncologists. Each breast cancer treatment hospital in India has a team of onco-surgeons, radiation oncologists, and medical oncologists.
Each type of oncologist listed above performs a separate set of duties religiously. A majority of breast cancer doctors in India are trained and educated from abroad. Additionally, they hold several certifications from some of the most prestigious organizations.
List of some Indian breast cancer surgeons include the following:
Six Simple Steps
Our medical advisory platform automatically sends your medical query to our network of expert Doctors, working only at top internationally accredited Hospitals.
You and the medical providers communicate directly via email or your online patient account; our case managers are always available to help you with this.
You receive medical opinions and cost estimates within 24 to 48 hours via email and your online patient account.
Lyfboat empowers you to compare the medical opinions, and discuss the options with our very own doctors who help answer your questions, and guide you in making informed decisions on the best treatment option.
We negotiate your final costs, explore available discount offers, and we handle all your logistics including travel, accommodation, transport, and medical co-ordination.
Get cured, pay hospital after treatment and return home safe. Our care team is available throughout your journey to good health!

Verified By Dr. Surbhi Suden
Dr. Surbhi Suden is one of the founders of Lyfboat and a doctor with a renowned name in the Medical tourism industry. She has been working with international patients since 2008 and is a deeply committed professional with a long term vision of transforming the current healthcare scenarios.Cost Calculator

Top Specialities
- Best Doctors in India
- Best Bariatric Surgeons in India
- Best Bone Marrow Transplant Doctor in India
- Best Cardiologist in India
- Best ENT Doctor in India
- Best Epilepsy Doctors in India
- Best Gastroenterologist in India
- Best Hair Transplant Surgeon in India
- Best Hematologist in India
- Best Hip Replacement Surgeon in India
- Best Infertility Doctor in India
- Best Knee Replacement Surgeon in India
- Best Liver Transplant Surgeon in India
- Best Nephrologist in India
- Best Neurologist in India
- Best Neurosurgeon in India
- Best Oncologist in India
- Best Orthopedic Doctor in india
- Best Ophthalmologist in India
- Best Penile Implant Surgeon in India
- Best Penile Enlargement Doctor in India
- Best Plastic Surgeon in India
- Best Pulmonologist in India
- Best Rhinoplasty Surgeon in India
- Best Rhinoplasty Surgeon in Turkey
- Best Spine Surgeon in India
- Best Urologist in India
- Best Cardiologists in the World
Top Treatments
- Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in Turkey
- Gastric Band Cost Turkey
- Cochlear Implant Surgery Cost in India
- Cancer Treatment Cost in India
- Erectile Dysfunction Treatment Cost in India
- Hair Transplant Cost in India
- Laser Eye Surgery Cost in India
- Penile Implant Surgery Cost in India
- Penis Enlargement Surgery Cost in India
- Spine Surgery Cost In India
- 5000 Grafts Hair Transplant Cost Turkey
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery in Turkey
- Turkey Hair Transplant Package
- Liver Transplant in Turkey
- Penis Enlargement in Turkey
- Kidney Transplant Cost in Turkey
- Knee Replacement in Turkey
- IVF Cost in Turkey
- Proton Beam Therapy Cost in India
- LVAD Cost in India
- Pediatric Liver Transplant Cost in India
- Limb Lengthening Surgery Cost in Turkey
- 5000 Grafts Hair Transplant Cost Turkey
- 5000 Grafts Hair Transplant Cost
- Liver Transplant Success Rate in India
- Liver Cancer Treatment Cost
- Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Cost
- Prostate Cancer Treatment Cost
Best Hospitals for Top Treatments
- Best Blood Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Bone Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Bone Marrow Transplant Hospitals in India
- Best Breast Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Cancer Hospitals in India
- Best Hospital for Brain Tumor in India
- Best Hip Replacement Hospital in India
- Best Heart Hospital in India
- Best Kidney Transplant Hospital in India
- Best Knee Replacement Hospital in India
- Best Liver Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
- Best Lung Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Neurology Hospital in India
- Best Orthopedic Hospital in India
- Best Spine Hospitals in India
- Best IVF Centre in India
- Best IVF Clinics in Turkey
- Best Hair Transplant Clinic in Turkey
- Best Prostate Cancer Hospital in India
- Best Hospital for Cyberknife Treatment in India
- Best Urology Hospital in India
- Best Hospitals for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in India
- Best ENT Hospital in India
- Best Kidney Transplant Hospitals in Turkey
- Best Hematology Hospital in India
- Best Lymphoma Treatment Hospitals in India
Latest Articles
- Best Countries for Plastic Surgery
- Best Countries for IVF
- Best Countries for Hair Transplant
- Blood Cancer Treatment Cost
- Brain Tumor Surgery Cost
- Robotic Heart Surgery Cost
- Knee Replacement Surgery Cost
- Penis Enlargement Surgery Cost
- Penile Implant Surgery Cost
- Liver Transplant Cost
- Gastric Band Abroad
- Tummy Tuck Abroad
- Gamma Knife Surgery Cost
- Spinal Fusion Surgery Cost
- Gastric Sleeve Abroad
- Gastric Bypass Abroad
- Scoliosis Surgery Cost
- Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Cost
- Life Expectancy After Kidney Transplant
- Best Country for Rhinoplasty
- Bone Marrow Transplant Success Rate
- Bone Marrow Transplant Cost
- Best Countries for Breast Augmentation
- Heart Bypass Surgery Cost
- Best Country for Cancer Treatment
- Hip Replacement Surgery Cost
- Kidney Transplant Cost
- Breast Cancer Treatment Cost
Disclaimer: Lyfboat does not provide professional medical opinion on the treatment or diagnosis of a particular ailment. All the offered services and information presented on www.lyfboat.com are only for the purpose of public knowledge and cannot substitute the professional consultation of the physician. Lyfboat strongly advice against copying or cloning of its web content and follows the legal protocols for protection of its intellectual property.
© 2024 Lyfboat Technologies Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Please wait








