Bone marrow transplant Donor in India
An individual is eligible to become a BMT donor if they are histocompatible with the patient. This means that their genetic makeup closely resembles that of the patient. Generally, a matching donor is from the immediate family, a child, a sister or brother, or a parent.
However, a patient can also get the best match through an unrelated donor. A cent-percent match is not necessary, but a close match for a positive outcome is indispensable.
The ideal BMT donor should:
- Be between 18 and 44 years of age
- Not have a BMI more than 35 and less than 18
- Not suffer from any mental illness
- Not suffer from any neurological disease
- Not suffer from chronic heart or lung conditions
- Not suffer from diabetes
- Not suffer from any blood disorder
- Not suffer from infections such as HIV, Hepatitis C, Syphilis, etc.
- Not be pregnant
Becoming a BMT Donor in India
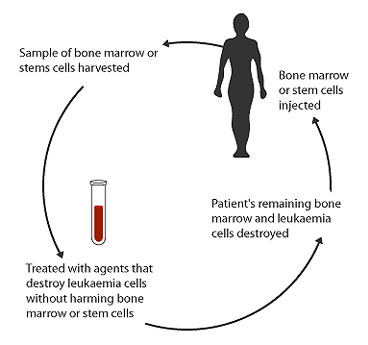
- If an individual decides to donate their bone marrow or stem cells (Both for a related or unrelated patient/recipient), they will have to undergo a comprehensive evaluation with a doctor to check their eligibility.
- The donor will be informed about the risks and complications associated with the procedure and inquired about their medical history. This will include a series of tests to screen possible genetic or infectious diseases.
- If the doctor deems the donor to be eligible for donation, they will undergo an HLA typing test to check the histocompatibility with the patient.
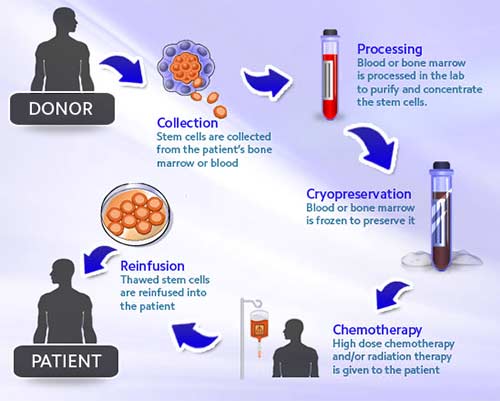
- There are two ways through which stem cells can be extracted from the donor’s body. These include:
Type of Donation | Bone Marrow Donation | Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Donation |
What does it involve? | The donor will undergo a surgery that will require an overnight hospital stay. The surgeon will insert a needle in the posterior region of the pelvic bone and aspirate a portion of the marrow. The surgery will be performed under anesthesia. | This type of donation is done as an outpatient procedure. The donor will be administered injections starting a few days before the procedure to promote stem cell number in the blood. On the day of the procedure, a catheter will draw blood out of the patient’s vein (usually arm), circulate it in a machine, and send it back into the patient’s body. The machine filters out stem cells from the blood and this process is called as apheresis. |
Time taken for the donation | 1 to 2 Hours | 2 Hours (May require more sittings, depending on the number of stem cells required by the patient.) |
Recovery | 3 to 4 Weeks | 7 to 14 Days |
Risks or Complications | Soreness in the treated area and difficulty in walking for a few days. | Bone pain, Muscle ache, nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue, and infection (in rare instances). |
Finding a BMT Donor in India
Finding a BMT donor in India can be quite challenging. The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) doesn’t include a registry for this specific category. There are a few independent organizations like MDRI and Daitri that provide these services and information.
Patients can register their details and find the best possible match. On the other hand, if anyone wishes to list themselves as a donor, they too can register and share necessary details for future reference.