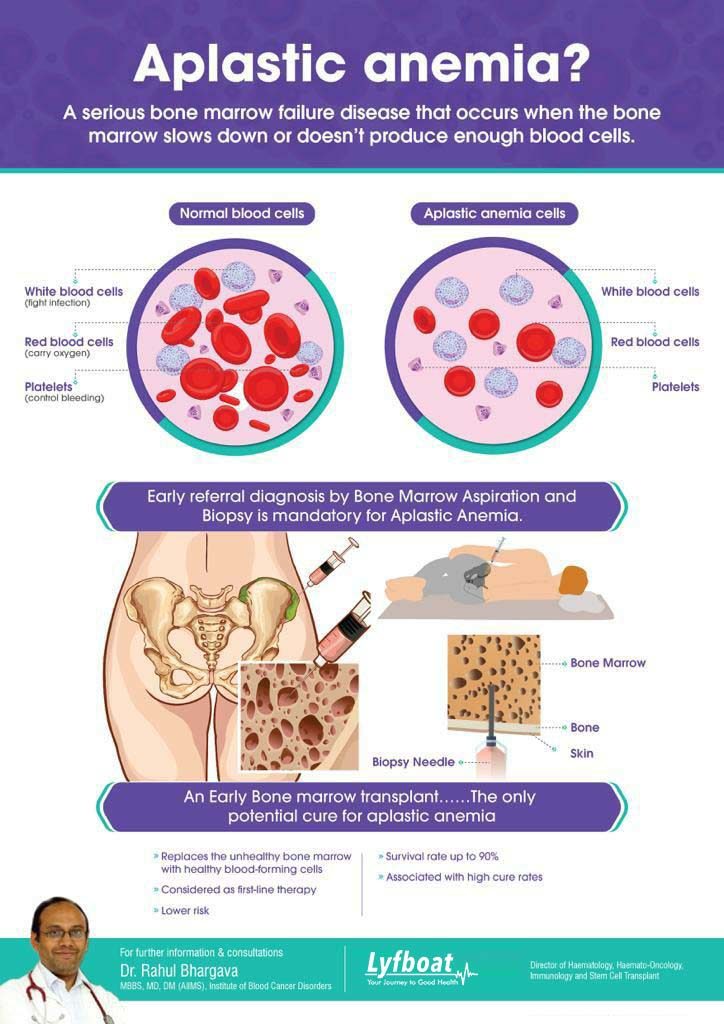
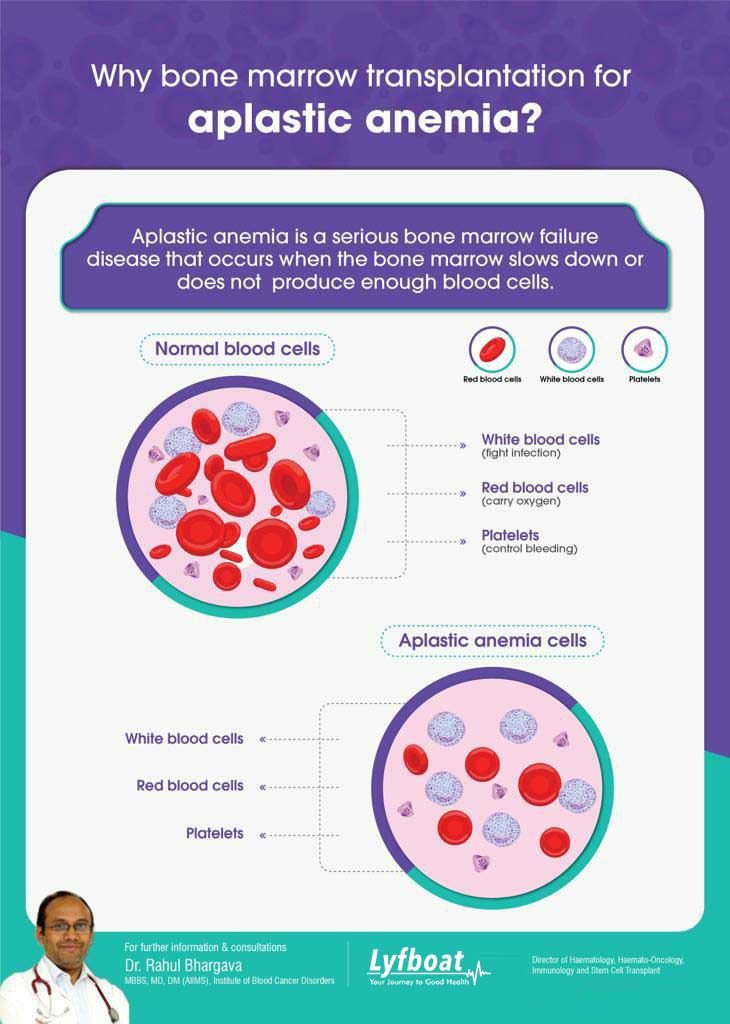
Blood Cell Formation And Types
Your blood is made of various types of cells suspended in a fluid called plasma which is made up primarily of water and contains proteins, nutrients, hormones and other chemicals that are vital to your bodies proper function and health.
Blood cells come in three distinct forms each with its own unique function:
- Red Cells (RBCs) – Also known as erythrocytes, the red blood cells are filled with hemoglobin, a type of protein that transports oxygen from the lungs throughout the rest of the body. RBCs make up approximately half of the blood cells in the body.
- White Cells (WBCs) – White blood cells, or leukocytes, serve as an important part of the immune system by fighting the germs that cause infection and other illnesses. WBCs come in a variety of forms each specialized to defend the body against specific types of germs.
- Platelets – Platelets, or thrombocytes, aid in blood clotting to allow the wounds to stop bleeding. Without platelets, and the ability to clot, even a minor cut would bleed indefinitely.
All blood cells are created inside spongy bone marrow that is inside certain bones. The stem cells in the bone marrow can develop into any of the three types of blood cell. Once the cell is mature it leaves the bone marrow and enters the bloodstream. In healthy individuals, the stem cells inside the bone marrow produce sufficient healthy cells. On rare occasions, however, there can be a failure in the bone marrow which leads to certain blood disorders such as Aplastic Anemia.